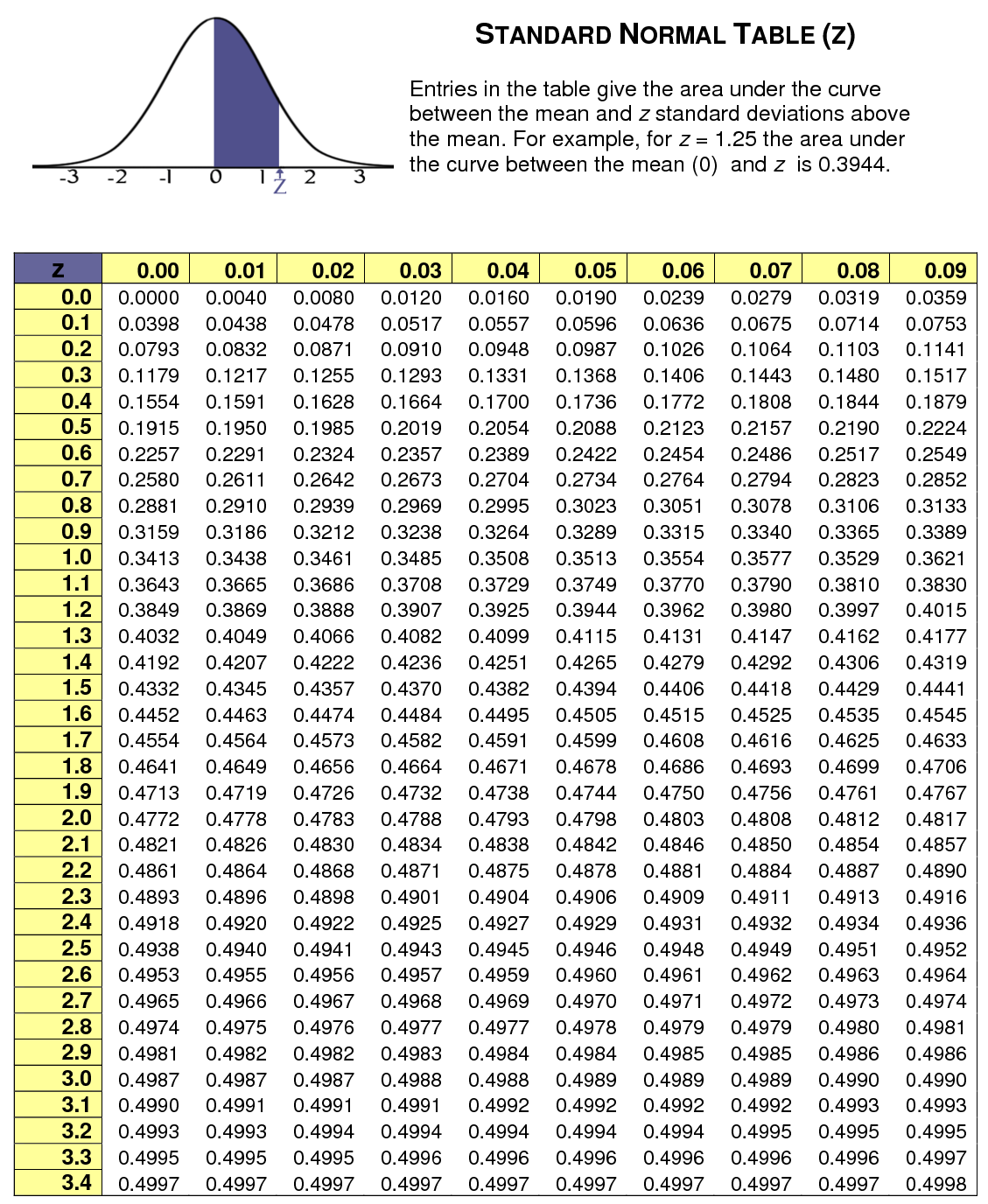
Use this standard normal distribution table (same as z score table, z table, normal distribution table or z chart) to find an area between the mean and Z score standard deviation. For negative negative z score table values just add a “-” sign.

You can also use this z score calculator to generate a z score
Population Mean : Population standard deviation :Related Calculators
Simply put, a z score table which is also known as the standard normal table is a table that allows you to know the percentage of values below (to the left) a z score is in a standard normal distribution.
Notice that it is important that you keep in mind that a z score (which is also known as the standard score) is a value that indicates the number of standard deviations a raw score has above or below the mean.
It is also worth to point out that when you need to calculate the mean of the z score, it will always be equal to zero as well as the standard deviation or variance will always be in increments of one.
One of the things that you need to know about the z score table is that this table shows the percentage of values using, in most cases, a decimal figure). Notice that these values to the left of a given z score on a standard normal distribution.
Let’s see an example. Let’s imagine that you got a z score of 1.09. So, the first thing that you will need to do is to look at the left of the side column of the z table to discover the value corresponding to one decimal place of the z-score. For example, the whole number and the first digit after the decimal point).
In this example that we are considering, this number is 1. Then, you will need to look up at the remaining number across the table on the top. In this case, we are looking for the 0.09. Som you can then easily see that the corresponding area is 0.8621 which translates into 86.21% of the standard normal distribution being below (or to the left) of the z-score.
Again, when you are trying to find the area to the right of a positive z score, you will need to start reading off the area in the z score table for normal distribution.
Considering that the total area under the bell curve is always 1 (which is equivalent to say that is 100%), you will need to subtract the area from the z score table for normal distribution from 1.
Let’s continue with the same example and say that you have a z score of 1.09. So, since you are trying to find the area to the right of a positive z score, you will need to:
1 – 0.8621. = 0.1379, since you already knew that 0.8621 was the area to the left of z = 1.09.
Many students usually deal with many difficulties when they see a negative z score. However, you just need to keep in mind that you can disregard the negative sign and then simply subtract the area from the table from 1.
 score table for normal distribution" width="400" height="272" />
score table for normal distribution" width="400" height="272" />
Again, and just like what we explained in the above case, when you have a negative z score, you can disregard the negative sign.
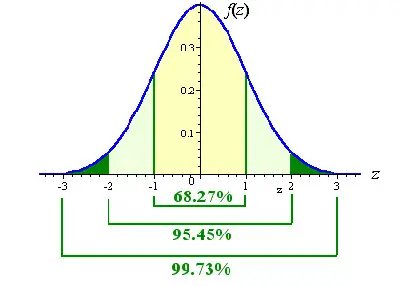
When you are trying to find the area between two negative z scores, you will need to perform a few more calculations. The truth is that you will be trying to discover the area or proportion of the standard normal distribution to the left of the lowest z score value as well as the area or proportion of the standard normal distribution to the right of the highest z score value.
As soon as you can determine these two values, you will need to add them together and then subtract them from 1 since 1 is the total area of the standard normal distribution.
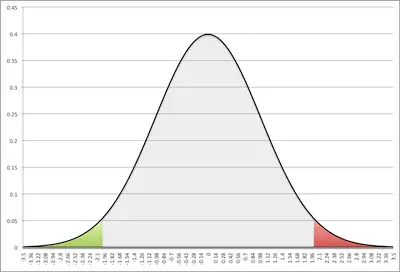
If you remember, the total area under any normal curve (including the standardized normal curve) is 1. So, we can then state that:
However, if you take the time to observe, you will b able to see that you just got the same value as for p(Z > 2.13). This happens because we are dealing with a normal distribution which is always symmetrical. So the tail of the curve below –2.13 representing p(Z < –2.13) looks exactly like the tail above 2.13 representing p(Z > +2.13).